Status for: Vegetation Indices (MOD13)
Validation at stage 3 has been achieved for the MODIS Vegetation Index (VI) product suite
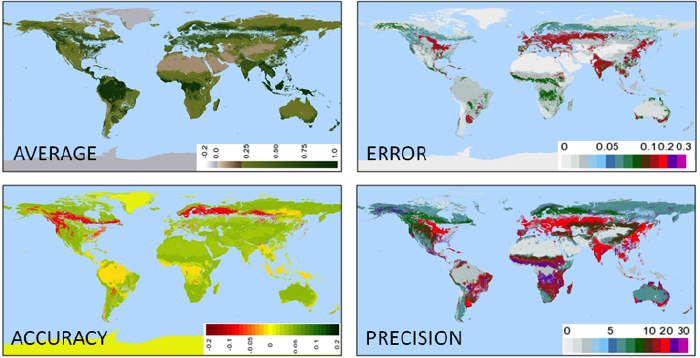
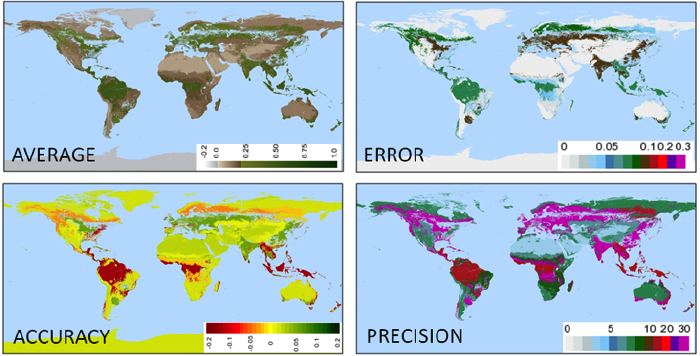
Accuracy is now within ± 0.025, which represents the ability of the 16-day VI products to retrieve a top of canopy (TOC) and nadir VI value when observations are of high quality (clear, no sub pixel cloud, low aerosol, and sensor view angle < 30 degrees). This estimate is based on comparisons with AERONET-corrected data, other space and airborne sensors, and radiometric field measurements over a range of biomes and seasonality. The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) accuracy is within ± 0.025, while that of the enhanced VI (EVI) is within ± 0.015, and the accuracy of retrieving TOC VI for a good quality day (high quality without the nadir view requirement) would be to within ±0.020 for NDVI and ± 0.010 for EVI. Errors in the red band associated with residual atmospheric effects are the main source of the NDVI errors. The blue band is helpful to correct the red band bias and reduce errors in EVI. When the per-pixel quality information is uncertain or erroneous (omission or commission errors) the overall NDVI and EVI errors increase to about 0.04-0.1 (VI units). This larger error envelope captures the sum of all error sources (sensor, atmosphere correction, and uncertainty in quality) and as such is the more general global error envelope for the MODIS VI time series.
The MODIS VI is retrieved from daily, atmosphere-corrected, bidirectional surface reflectance. The VIs are generated at 16-day intervals using a MODIS-specific compositing method based on product quality assurance to remove low quality observations. From the remaining good quality VI values, a constrained view angle approach then selects a pixel to represent the compositing period (from the two highest NDVI values it uses the pixel that is closer-to-nadir). Because the MODIS sensors aboard Terra and Aqua satellites are identical the VI algorithm generates the respective 16-day composite eight days apart (phased production) to permit the combination of both sensor data into a seamless record. The MODIS VI product suite is now used frequently in ecosystem, climate, and natural resources management studies and operational research as demonstrated by the increasing body of peer-reviewed publications.
Overall, the NDVI-based compositing criteria results in a small positive bias (+0.020) in NDVI, since forward-scatter pixels may be preferentially selected, but an insignificant bias in the EVI values. All VI values are computed in the same way in time and space, regardless of land cover and soil type, and represent true surface measurements (not modeled and no assumptions) that can be readily validated. For most cloud- and snow-free pixels with low aerosol load, the VI values are very accurate, however, for cases when there are no pixels of acceptable quality available within a compositing period, a lower quality observation with the maximum NDVI will be chosen to gap-fill the pixel. The VI product is particularly dependent upon coherent inter-band (blue, red and NIR) atmospheric correction and thus may be unstable over extreme bright or dark surfaces, such as snow, desert playas, and inland water bodies, where the VI values should be used with caution.
Analyses from various airborne and field validation campaigns demonstrate that over most biomes, MODIS near-nadir satellite VI have very good agreement with top-of-canopy nadir VI and with land surface biophysical properties. Comparisons of seasonal MODIS VI with seasonal flux tower (FLUXNET) measurements of gross primary production show very strong agreement across a global set of biome types. MODIS VI values have also been found to be in good agreement with VI computed from the MODIS Nadir BRDF-Adjusted Reflectance (NBAR) product (MCD43A4), 8-day surface reflectance (MOD09), as well as with VIs generated from the ASTER and Landsat ETM+, OLI, and S-NPP VIIRS sensors. MODIS NDVI exhibits saturation in dense vegetation canopies, including forests, while MODIS EVI maintains good sensitivity and correlation with tower flux measurements of photosynthesis in high biomass regions.
Users are advised to examine the per-pixel product quality information to screen poor quality data before use in applications, science, or research. Poor quality inputs to the VI algorithm usually result in abnormally low VI values, however, anomalous high values may also occur, particularly with EVI over snow and cloud and NDVI and EVI near or over water bodies.
Product version: Collection 6
| Title: Application and Comparison of the MODIS-Derived Enhanced Vegetation Index to VIIRS, Landsat 5 TM and Landsat 8 OLI Platforms: A Case Study in the Arid Colorado River Delta, Mexico. |
| Author: Jarchow CJ, Didan K, Barreto-Muñoz A, Nagler PL, Glenn EP |
| Source: Sensors. 2018 May 13;18(5):1546 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Transitioning from MODIS to VIIRS: an analysis of inter-consistency of NDVI data sets for agricultural monitoring |
| Author: Skakun, S., Justice, C.O., Vermote, E., Roger, J.C. |
| Source: International Journal of Remote Sensing. 2018 Feb 16;39(4):971-92 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Ecosystem resilience despite large-scale altered hydroclimatic conditions |
| Author: Guillermo E. Ponce-Campos, Moran, M. S., Huete, A., Zhang, Y., Bresloff, C., Huxman, T. E., Eamus, D., Bosch, D. D., Buda, A. R., Gunter, S. A., Scalley, T. H., Kitchen, S.G., McClaran, M. P., McNab, W. H., Montoya, D. S., Morgan, J. A., Peters, D. PC, Sadler, E. J., Seyfried, M. S., Starks, P. J. |
| Source: Nature 494, no. 7437 (2013): 349-352 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Multi-angle implementation of atmospheric correction for MODIS (MAIAC): 3. Atmospheric correction |
| Author: Alexei Lyapustin, Yujie Wang, Istvan Laszlo, Thomas Hilker, Forrest G Hall, Piers J. Sellers, Compton J. Tucker, and Sergey V. Korkin. |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment 127 (2012): 385-393 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: A comparison of Landsat TM and MODIS vegetation indices for estimating forage phenology in desert bighorn sheep (Ovis canadensis nelsoni) habitat in the Sonoran Desert, USA. |
| Author: Steven Edward Sesnie, Brett Gary Dickson, Steven Sheldon Rosenstock, and Jill Marie Rundall |
| Source: International Journal of Remote Sensing 33, no. 1 (2012): 276-286. |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Seasonal and inter-annual variation in view angle effects on MODIS vegetation indices at three forest sites. |
| Author: Daniel A. Sims, Abdullah F. Rahman, Eric F. Vermote, and Zuoning Jiang |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment 115, no. 12 (2011): 3112-3120. |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Exploring the potential of MODIS EVI for modeling gross primary production across African ecosystems. |
| Author: Martin Sjöström, Jonas Ardö, Almut Arneth, N. Boulain, Bernard Cappelaere, Lars Eklundh, A. De Grandcourt, W.L. Kutsch, L. Merbold, Y. Nouvellon, R.J. Scholes, P. Schubert, J. Seaquist, E.M. Veenendaal |
| Source: Remote sensing of environment 115, no. 4 (2011): 1081-1089. |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Assessment of biases in MODIS surface reflectance due to Lambertian approximation. |
| Author: Yujie Wang, Alexei I. Lyapustin, Jeffrey L. Privette, Robert B. Cook, Suresh K. SanthanaVannan, Eric F. Vermote, and Crystal L. Schaaf |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment 114, no. 11 (2010): 2791-2801 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the US Central Great Plains. |
| Author: Brian D. Wardlow, Stephen L. Egbert, and Jude H. Kastens |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment 108, no. 3 (2007): 290-310. |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Multisensor Comparisons for Validation of MODIS Vegetation Indices |
| Author: Qian Cheng |
| Source: Pedosphere 16, no. 3 (2006): 362-370 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Assessment of MODIS-EVI, MODIS-NDVI and VEGETATION-NDVI composite data using agricultural measurements: An example at corn fields in western Mexico. |
| Author: Pei-Yu Chen, Gunar Fedosejevs, Mario Tiscareño-López, and Jeffrey G. Arnold |
| Source: Environmental monitoring and assessment 119, no. 1-3 (2006): 69-82. |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Time-series validation of MODIS land biophysical products in a Kalahari woodland |
| Author: Huemmrich, K.F., J. L. Privette, M. Mukelabai, R. B. Myneni, Y. Knyazikhin |
| Source: International Journal of Remote Sensing, 26(19), 4381-4398 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Multisensor comparisons and validation of MODIS vegetation indices at the semiarid Jornada Experimental Range |
| Author: Xiang Gao, Alfredo R. Huete, and Kamel Didan |
| Source: IEEE Transactions on Geoscience & Remote Sensing, 41(10):2368-2381 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices |
| Author: A. Huete, K. Didan, T. Miura, E.P. Rodriguez, X. Gao, L.G. Ferreira |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment, 83: 195-213 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Potential of MODIS EVI and surface temperature for directly estimating per-pixel ecosystem C fluxes |
| Author: Rahman, A.F., D. A. Sims, V. D. Cordova, and B. Z. El-Masri |
| Source: Geophys. Res. Lett. 32, L19404, doi:10.1029/2005GL024127 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: On the use of MODIS EVI to assess gross primary productivity of North American ecosystems |
| Author: Sims, D.A., A.F. Rahman, V.D. Cordova, B.Z. El-Masri, D.D. Baldocchi, L.B. Flanagan, A.H. Goldstein, D.Y. Hollinger, L. Misson, R.K. Monson, W.C. Oechel, H.P. Schmid, S.C. Wofsy, and L. Xu |
| Source: Journal of Geophysical Research VOL. 111, G04015, doi:10.1029/2006JG000162, 2006 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Amazon rainforests green-up with sunlight in dry season |
| Author: Huete, A.R., K. Didan, Y. E. Shimabukuro, P. Ratana, S.R. Saleska, L.R. Hutyra, D. Fitzjarrald, W. Yang, R.R. Nemani, and R. Myneni |
| Source: Geophysical Research Letters, 13, doi:10.1029/ 2005GL025583 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: A multi-scale analysis of dynamic optical signals in a Southern California chaparral ecosystem: A comparison of field, AVIRIS and MODIS data |
| Author: Cheng, Y., J.A. Gamon, D.A. Fuentes, Z. Mao, D.A. Sims, H. Qiu, H. Claudio, A. Huete, A.F. Rahman |
| Source: Remote Sens. Environ., 103, 369-378. |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Inter-Comparison of ASTER and MODIS Surface Reflectance and Vegetation Index Products for Synergistic Applications to Natural Resource Monitoring |
| Author: Tomoaki Miura, Hiroki Yoshioka, Kayo Fujiwara, Hirokazu Yamamoto |
| Source: Sensors 2008, 8, 2480-2499 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Multiple site tower flux and remote sensing comparisons of tropical forest dynamics in Monsoon Asia |
| Author: A.R. Huete, N. Restrepo-Coupe, P. Ratana, K. Didan, S.R. Saleska, K. Ichii, S. Panuthai, M. Gamog |
| Source: Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,148, (2008) 748-760 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |