Status for: Evapotranspiration (MOD16)
Stage 3 validation has been achieved for the MODIS Collection 6 evapotranspiration product (MOD16).
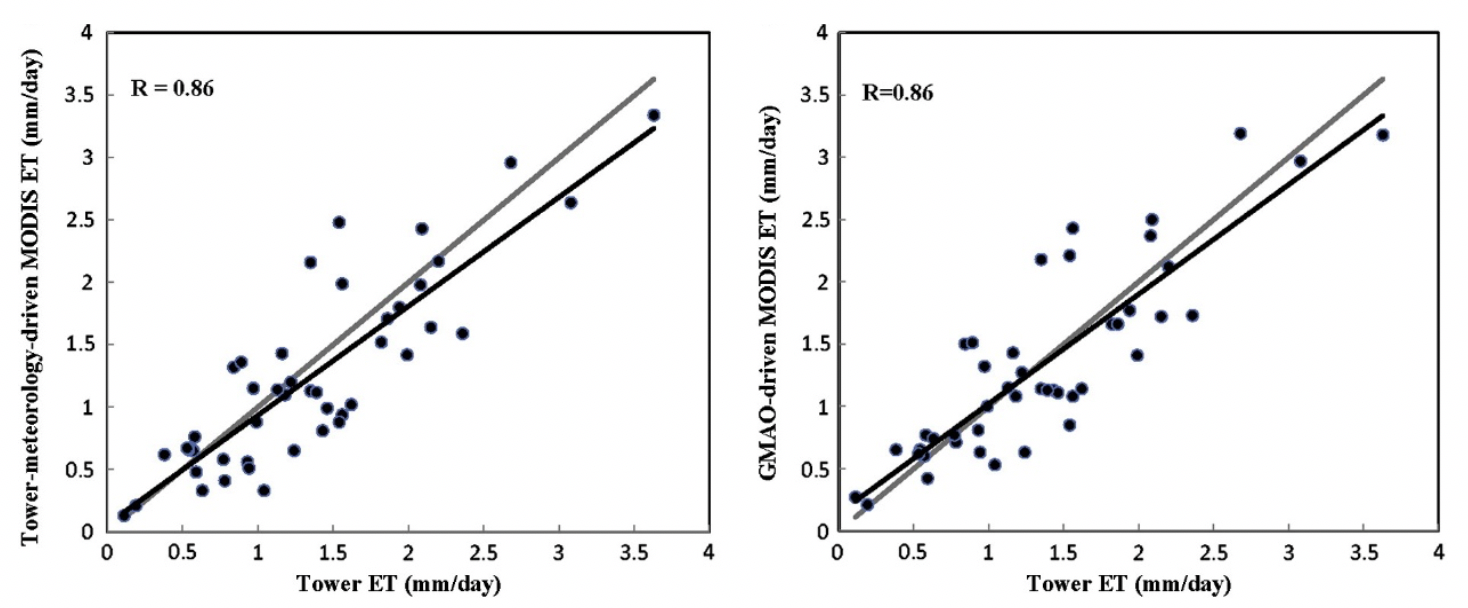
The mean absolute errors are 24% of the ET measurements, within the 10-30% range of the accuracy of ET observations (Mu et al, 2011). The correlation coefficients of the tower-specific improved ET estimates with the ET measurements averaged over all the available days is 0.86 when driven by NASA Goddard's Global Modeling and Assimilation Office (GMAO) meteorological data.
The MODIS evapotranspiration (ET) algorithm is based on the logic of the Penman-Monteith equation, which uses daily meteorological reanalysis data and 8-day remotely sensed vegetation property dynamics from MODIS as input. MOD16 Collection 6 products include terrestrial ecosystem evapotranspiration (ET), latent heat flux (LE), potential ET (PET), and potential LE (PLE) data layers and are produced at 500m spatial resolution.
To validate the MOD16 algorithm, we used the observed latent heat flux for 46 field-based eddy covariance flux towers over the 11 years (2000 to 2010), driven by two sets of meteorological data: tower-based meteorological data and GMAO meteorological data (Mu et al, 2011).
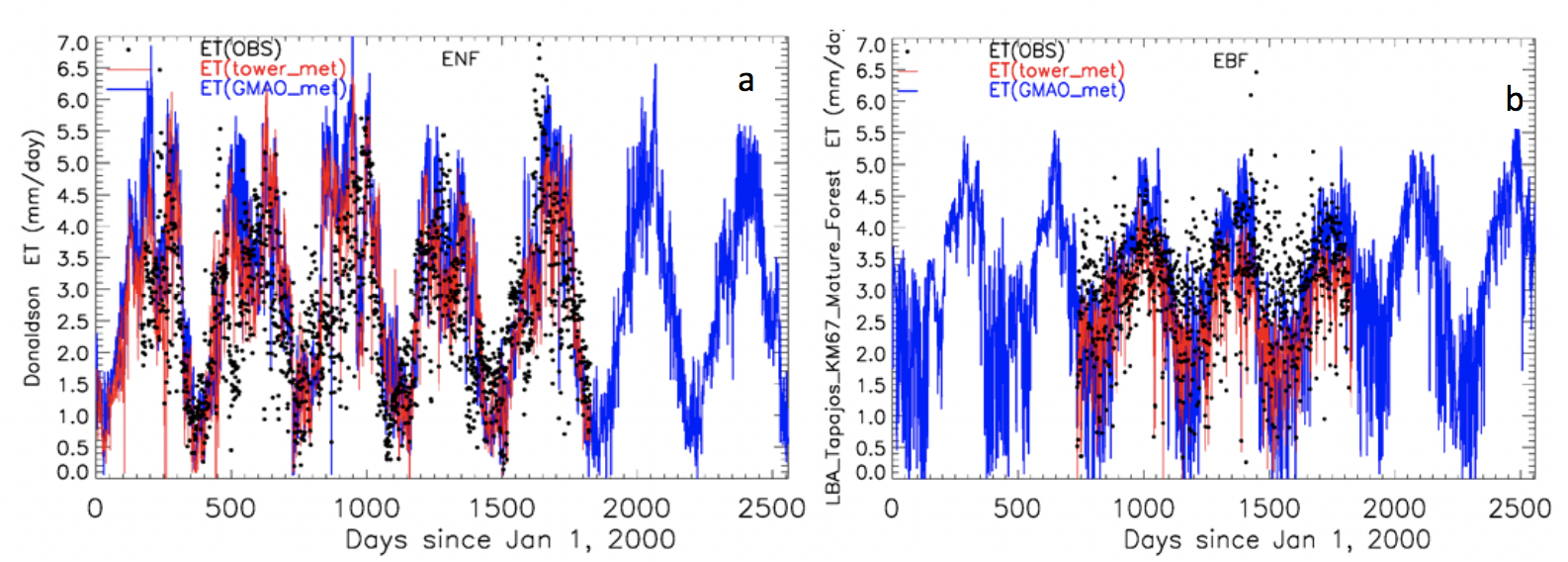
Micrometeorological tower sites use the eddy covariance technique to measure exchanges of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy between terrestrial ecosystems and the atmosphere. Their data have been used extensively for direct validation and optimization of many global water and carbon models. Figure 1 shows an example the validation carried out of the MOD16 ET algorithm for two selected sites, while Figure 2 compares average ET estimates by MOD16 and the 46 micrometeorological tower sites.
Product version: Collection 6.1
| Title: Comparison of the performance of latent heat flux products over southern hemisphere forest ecosystems: estimating latent heat flux error structure using in situ measurements and the triple collocation method |
| Author: Barraza Bernadas, V., Grings, F., Restrepo-Coupe, N. and Huete, A. |
| Source: International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39:19, 6300-6315, DOI: 10.1080/01431161.2018.1458348 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Multi-scale evaluation of global gross primary productivity and evapotranspiration products derived from Breathing Earth System Simulator (BESS) |
| Author: Jiang, C. and Ryu, Y. |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment, 186, pp.528-547 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Development of a coupled carbon and water model for estimating global gross primary productivity and evapotranspiration based on eddy flux and remote sensing data |
| Author: Zhang, Y., Song, C., Sun, G., Band, L.E., McNulty, S., Noormets, A., Zhang, Q. and Zhang, Z. |
| Source: Agricultural and forest meteorology, 223, pp.116-131 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Water balance_based actual evapotranspiration reconstruction from ground and satellite observations over the conterminous United States |
| Author: Wan, Z., Zhang, K., Xue, X., Hong, Z., Hong, Y. and Gourley, J.J. |
| Source: Water Resources Research, 51(8), pp.6485-6499 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Comparing evapotranspiration from eddy covariance measurements, water budgets, remote sensing, and land surface models over Canada |
| Author: Wang, S., Pan, M., Mu, Q., Shi, X., Mao, J., Brümmer, C., Jassal, R.S., Krishnan, P., Li, J. and Black, T.A. |
| Source: Journal of Hydrometeorology, 16(4), pp.1540-1560 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Comparison of different evaporation estimates over the African continent |
| Author: Trambauer, P., Dutra, E., Maskey, S., Werner, M., Pappenberger, F., Van Beek, L.P.H. and Uhlenbrook, S. |
| Source: Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 18(1), p.193 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Assessment of the MODIS global evapotranspiration algorithm using eddy covariance measurements and hydrological modelling in the Rio Grande basin |
| Author: Ruhoff, A.L., Paz, A.R., Aragao, L.E.O.C., Mu, Q., Malhi, Y., Collischonn, W., Rocha, H.R. and Running, S.W. |
| Source: Hydrological Sciences Journal, 58(8), pp.1658-1676 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Uncertainty in evapotranspiration from land surface modeling, remote sensing, and GRACE satellites. |
| Author: Long, D., Longuevergne, L. and Scanlon, B.R. |
| Source: Water Resources Research, 50(2), pp.1131-1151 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: A comprehensive evaluation of two MODIS evapotranspiration products over the conterminous United States: Using point and gridded FLUXNET and water balance ET |
| Author: Velpuri, N.M., Senay, G.B., Singh, R.K., Bohms, S. and Verdin, J.P. |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment, 139, pp.35-49 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Global estimates of evapotranspiration for climate studies using multi-sensor remote sensing data: Evaluation of three process-based approaches |
| Author: Vinukollu, R.K., Wood, E.F., Ferguson, C.R. and Fisher, J.B. |
| Source: Remote Sensing of Environment, Volume 115, Issue 3, Pages 801-823 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |
| Title: Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm |
| Author: Mu, Q., Zhao, M., & Running, S. W. |
| Source: J. Geophys. Res., 112, G01012, doi:10.1029/2006JG000179 |
| View Abstract and Access Publication |